Understanding the Symptoms and Treatments of Lumbar Disc Herniation
Lumbar disc herniation, a common spinal condition, involves the abnormal displacement of an intervertebral disc in the lumbar region. Understanding its symptoms and treatments is essential for effective pain management and potential complications.
By fully grasping early signs such as lower back pain and sciatica, individuals can take proactive steps to seek proper diagnosis and treatment. This knowledge also allows for choosing among various treatment options, ranging from conservative approaches to surgical interventions, to restore spinal health and functionality.
Understanding the Anatomy and Normal Functioning of the Lumbar Spine
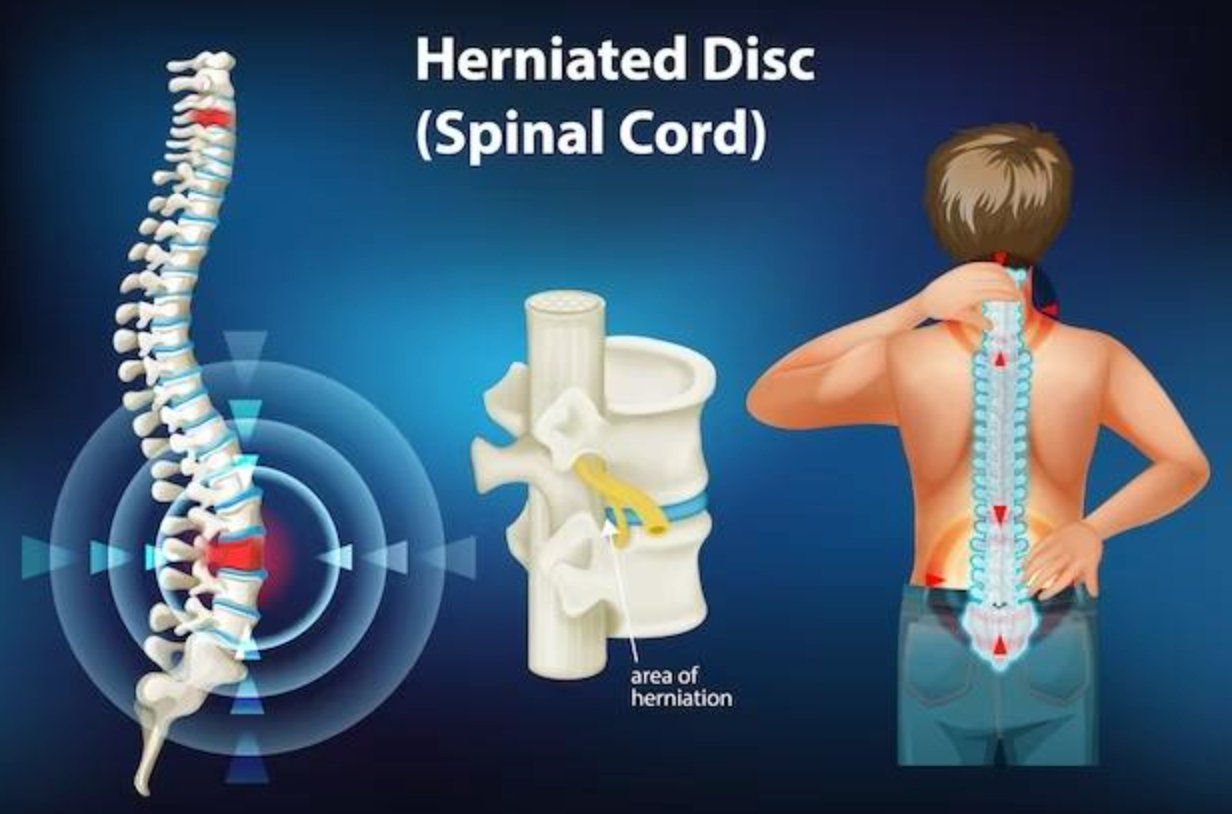
The lumbar spine, composed of five vertebrae, supports the lower back and facilitates movement. The intervertebral discs, located between each vertebra, absorb shocks and allow flexibility. Muscles, ligaments, and tendons provide additional support. The vertebral structure maintains stability while allowing various movements. Normal functioning involves balanced pressure distribution on the intervertebral discs during daily activities.
Understanding this anatomy is essential to recognize the symptoms of lumbar disc herniation. Symptoms may include lower back pain, leg pain, numbness, and weakness. Treatment depends on an accurate diagnosis and may include medication, physical therapy, or surgery. Preventive measures such as proper lifting techniques and ergonomic adjustments can reduce the risk of lumbar disc herniation. Overall, understanding the anatomy and function of the lumbar spine helps manage and prevent this condition.
Understanding the Symptoms of Lumbar Disc Herniation
Lumbar disc herniation symptoms include several distinctive signs. Firstly, lower back pain is often present, manifesting as a dull or sharp pain in the lower back region. Secondly, sciatica, pain radiating along the sciatic nerve, is common. This pain can spread to the buttocks, thighs, and even feet.
Additionally, numbness and muscle weakness may be felt in the legs, affecting mobility and sensation. Other associated symptoms may include tingling, a burning sensation, or difficulty standing or walking. It is crucial to recognize these symptoms early for effective treatment of lumbar disc herniation.
Diagnosing Lumbar Disc Herniation
Diagnosing lumbar disc herniation is crucial for identifying the symptoms associated with this condition and guiding appropriate treatment. Physical exams and diagnostic tests are used to evaluate patients presenting with lumbar disc herniation symptoms. During the physical exam, the doctor may look for signs such as tenderness of the lumbar spine, sensory disturbances, and muscle weakness. These tests help confirm the presence of lumbar disc herniation symptoms.
In addition to physical exams, medical imaging plays a crucial role in diagnosing lumbar disc herniation. MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) and CT (computed tomography) scans allow precise visualization of the lumbar spine's internal structures. These images can reveal the presence of a herniated disc and the extent of damage to surrounding tissues.
Through these advanced diagnostic techniques, doctors can establish an accurate diagnosis of lumbar disc herniation and develop a treatment plan tailored to each patient's specific needs. It is essential to consult a healthcare professional as soon as lumbar disc herniation symptoms appear to receive an appropriate diagnosis and begin proper treatment as early as possible.
Treatment Options for Lumbar Disc Herniation
Treatment for lumbar disc herniation can vary depending on the severity of the symptoms and patient preferences. Here is an overview of available treatment options:
A. Conservative Approaches
Pain relief and anti-inflammatory medications are often prescribed to alleviate pain and inflammation associated with lumbar disc herniation. These medications can help manage symptoms while promoting healing. Physical therapy and strengthening exercises are essential for building back muscles and improving spinal stability.
These treatments can help reduce pain and prevent recurrences of lumbar disc herniation. Alternative therapies such as acupuncture and chiropractic care can also be beneficial in managing lumbar disc herniation symptoms by relieving pain and improving mobility.
B. Invasive Treatments
Epidural injections can be used to deliver corticosteroids directly to the affected area of the spine. These injections can reduce inflammation and alleviate pain associated with lumbar disc herniation. Surgery for lumbar disc herniation may be considered if other treatments have not successfully relieved symptoms.
This intervention aims to remove the herniated disc fragment pressing on the surrounding nerves, which can help alleviate pain and restore functionality.
It is important to consult a healthcare professional to determine the best treatment plan for each individual case of lumbar disc herniation. By combining conservative approaches and, if necessary, invasive treatments, it is possible to effectively manage lumbar disc herniation symptoms and improve patients' quality of life.
Management and Prevention of Lumbar Disc Herniation
Effective management of lumbar disc herniation involves a holistic approach to reduce symptoms and prevent future injuries. A crucial first step is lifestyle and ergonomic modifications. This can include posture adjustments when lifting heavy objects, as well as adopting ergonomic positions at work and home to reduce pressure on the lumbar spine.
Additionally, injury prevention techniques should be implemented. This can involve an exercise program to strengthen back and core muscles, as well as stress relief techniques to reduce tension in the lumbar region. Medical follow-up and rehabilitation are also essential for effectively managing lumbar disc herniation. Regular follow-ups with a healthcare professional allow monitoring of symptoms and adjustments to the treatment plan as needed. Rehabilitation may include physical therapy sessions to strengthen surrounding muscles and improve flexibility.
Special Case: Lumbar Disc Herniation in Athletes and Manual Workers
Athletes and manual workers are often at increased risk of lumbar disc herniation due to repetitive movements and heavy lifting. For these groups, specific prevention is necessary, including training programs to strengthen back muscles and proper lifting techniques.
Regarding treatment, adapted approaches are necessary to meet the specific needs of these populations. This may include specialized rehabilitation techniques to promote rapid recovery and safe return to physical activity or work.
In summary, effective management of lumbar disc herniation requires a proactive approach focused on lifestyle modification, injury prevention, regular medical follow-up, and specific strategies for athletes and manual workers.
Conclusion
In conclusion, managing lumbar disc herniation requires a comprehensive approach, including lifestyle modification, injury prevention, and regular medical follow-up. Understanding the symptoms and treatments is crucial for ensuring effective management of this condition. By quickly recognizing the signs and implementing appropriate interventions, it is possible to improve patients' quality of life and minimize long-term complication risks.


Leave a comment
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.